
The interaction effect indicates that one factor impacts the relationship between the dependent variable and the other categorical variable.īased on that, there are two types of ANOVA tests we can run for the categorical variables – with and without Interaction. However, this is less informative as we can’t test for Interaction, and often have to assume there is none. We can also perform the analysis without replication, where we only have a single measurement for each arrangement of the factors. We usually run the Two-Way ANOVA model with replication, meaning that there is more than one observation for each combination of the independent variables. The model uses sample data to infer the characteristics of the entire population. If the variance within the groups is smaller than the overall variance, the F-value will be higher, meaning the observed difference is most likely real, and not due to chance.ĪNOVA is a test of hypotheses that we use to evaluate the differences between group means.
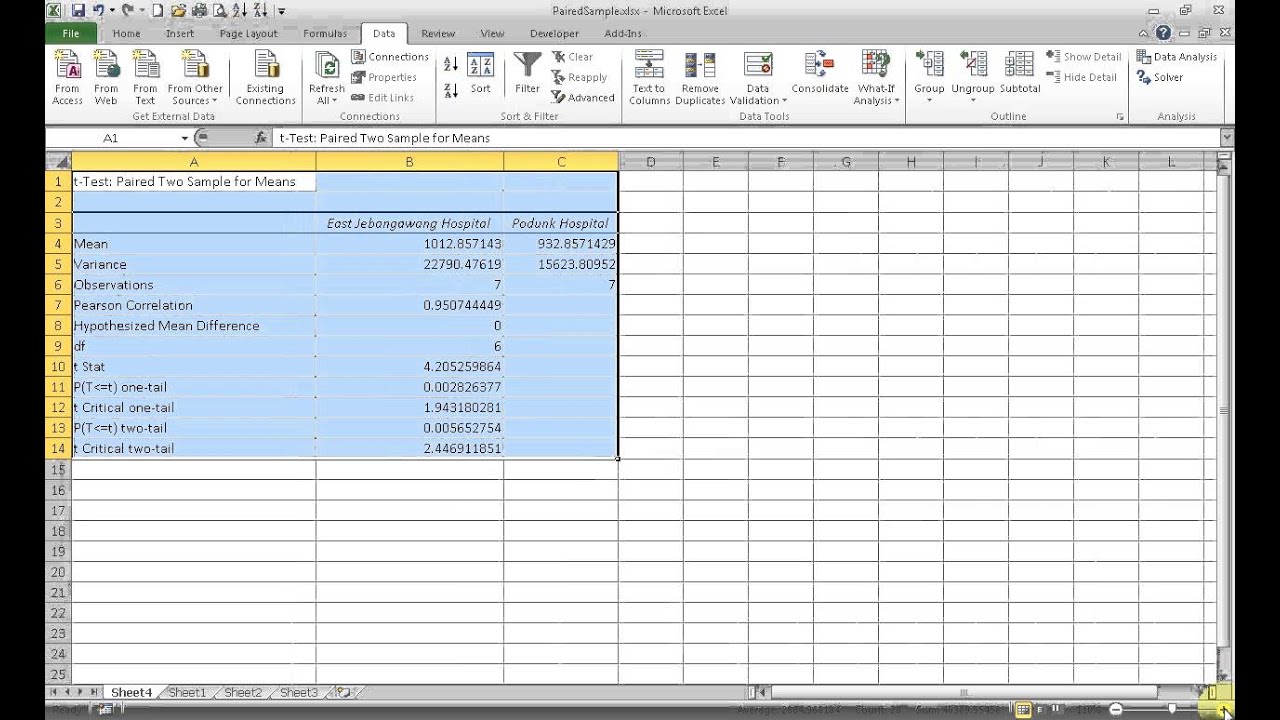
The F-test is a comparison test, which compares the variance in each group’s mean value to the overall variance in the dependent variable. The Analysis of Variance model relies on an F-test to check statistical significance. Observations need to be of sufficient quantity so that we can calculate an average for each combination of the levels in the categorical metrics. The quantitative metric should be one for which we can take measures and calculate a mean (average). They divide the dependent variable’s observations into groups for each combination of the categories. To run the Two-Way ANOVA model, we need to collect data on the quantitative dependent variable at different combinations (levels) of two independent categorical variables.Įach categorical value should have finite possible values or factor levels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
